
Forex trading (also ‘Foreign exchange’ or ‘FX’) is the buying and selling of one currency for another. Trades are placed based on the exchange rate listed on over the counter (OTC) or exchange traded platforms.
The market is the largest in the world, seeing over $5 trillion of trading each day. Forex can be traded five days a week, around the clock. There is no central exchange for currencies, so they are traded across the globe at various sources.
In each currency pair, the first currency listed is the ‘base’ currency, and the second the buying currency. So with EUR/USD the price quoted will be how many US dollars are required to purchase 1 Euro.
Almost all financial news, or global events, will influence forex prices. With markets available 24 hours a day and many brokers offering low commission, tight spreads and high leverage, forex trading has become extremely popular with retail investors.
It remains however, high risk, particularly where leverage is involved.
Top 5 Forex Brokers
Forex Charts
Most brokers offer live forex charts. But ensure you are dealing with genuine live prices, and not prices delayed by 15 minutes.
How Forex Pairs Work
Forex pairs are the starting point for forex trading. A ‘pair’ is the two currencies that are going to be traded. So a trader is going to buy one currency, using the other. So for example, with the GBP/USD pair. The trader will buy pounds, using the US dollar.
When prices are quoted, they are always the second currency, buying the first. So with EUR/GBP for example, the price quoted is the cost in pounds, to buy 1 Euro.
Note however, that the decimal will move, making the price look a little strange to anyone used to exchanging currency for their holiday. In the EUR/GBP example, the rate for trading is currently 8454.8.
For holiday makers heading to Europe, that equates to 84.5 pence buying 1 Euro.
The currency of the trading account does not matter, the broker will convert them as required in order to allow traders to buy or sell currencies. Retail forex trading is simply speculating on the movement of the exchange rates between forex pairs.
Which are the major forex pairs?
- EUR/USD
- USD/JPY
- GBP/USD
- USD/CHF
Established pairs, traded in high volume and based on the US dollar, are known as the ‘major’ pairs. In addition to these more traditional forex pairs, there is fast becoming a much broader range of currencies to trade – these are referred to as ‘minor’ or ‘exotic’ pairs.
Binary options brokers are now offering options on between 40 and 50 different currency pairs from all over the globe. Emerging markets have added a whole new element to Forex trading.
These markets include regions like South America and Asia. Currencies often represent the market confidence in the entire economy of the area concerned. Given the huge range of factors that contribute to such economies, it is easy to see why prices fluctuate constantly.
Minor and exotic pairs do however, see lower levels of trading volume, which can impact volatility, but also availability at times.
What are exotic forex pairs?
- TRY – Turkish lira
- NOK – Norwegian Krone
- SEK – Swedish Krone
- HKD – Hong Kong dollare
What Influences the Forex Markets?
So what influences the FX markets? Pretty much everything. Almost every piece of global news could have a conceivable impact on currency prices. For example, the collapse in the price of oil led to a similar fall in the value of the Russian rouble.
An economy so heavily linked with oil will rise or fall with the value of that commodity. There are additional factors to consider of course, but the example is clear.
A more subtle example was the Indian rupee. New governorship at the Reserve Bank of India boosted investor confidence in the recovery plans set out for the Indian currency.
That confidence was reflected in the resulting strong performance of the rupee. While India’s currency benefited directly, other Asian currencies drifted upwards as well, with regional performance a factor which helped both the Philippine peso and Thai baht.
Another example is foreign policy. If a nation such as China were to broker a deal with Russia over gas, both currencies may benefit. If markets believed one trade partner has the better side of the deal then one currency may gain while another suffers.
Traders may take a view on future foreign policy and invest accordingly. These examples are some of the more obvious and larger market drivers, but illustrate the fact that forex is a very complex market.
Volatility in the Forex markets
Uncertainty in markets usually leads to volatility. The global economy is without doubt uncertain right now, meaning there are plenty of opportunities for Forex traders.
Binary options provide an opportunity to profit from the uncertainty. The range of forex currencies available to trade via binary options brokers has never been bigger and the right strategy, for the right currency, could prove very profitable. Our reviews highlight those brokers that focus on exchange rate binary options.
Forex Markets Opening Hours
Some beginners skip some forex basics and head straight for strategy. That can be a mistake, and lead to a lot of lessons learnt the hard way (losing trades). One such ‘fundamental’, is knowing the hours when certain markets will be open.
The forex market is open 24-hours a day. This is because banks and corporation are open at different times around the world. This demand provides liquidity to forex pairs. Yet each hour of the day has different tendencies based on what part of the globe is open for business. Understand forex market hours, and hourly tendencies, and you’ll be better able to apply your strategies at opportune times.
Forex Market Sessions
Major markets are open at different times throughout the day. Which market(s) is open directly affects the liquidity and volatility and forex pairs.
The EURUSD for example is most liquid and volatile during the London and New York sessions, especially during the “overlap” period when London and New York are both trading.
The USDJPY typically has the most volatility when Tokyo first opens, and when New York opens many hours later.
Currencies generally see increased liquidity when one or more markets that actively trade, or use, that currency are open for business.
Here are the forex sessions based on GMT for UK Traders:
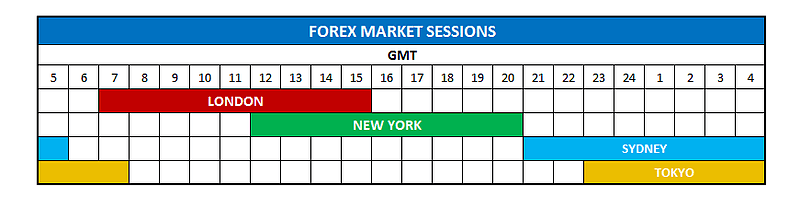
The chart does not show every market in the world. But those shown are the major markets for forex. The Canadian market is open while New York is open, and London overlaps with other European markets.
Germany opens one hour before London; therefore, some consider that to be the open, and not the start of the London session. Volatility, on average, doesn’t see a marked increased until London opens though.
Intra-Day Volatility
Those major sessions directly impact currency pair volatility. Hourly volatility does follow certain trends. If your strategy is based on volatility or you are using a trending strategy, focus on times of day where the price moves are largest.
If you are using more of a range trading strategy, or prefer low volatility, trade during the sedate times. Check where the charts show decreased hourly volatility.
08:00 to 17:00 GMT provide the best trending opportunities, with 13:00 to 17:00 generally providing the biggest moves.
Those seeking reduced volatility, or times more likely to quietly range, trade between 20:00 and 05:00 GMT.
The USDCHF is very similar to the EURUSD in terms of its hourly volatility structure, although the USDCHF moves less overall each day and therefore overall hourly volatility is several pips less.
The NZDUSD has very similar hourly volatility to the AUDUSD, and they both move roughly the same amount each day.
Opening Hours Conclusions
Learning the basics, like what the market sessions and hours mean to you as a trader, can significantly help in strategy and timing. No matter what time frame you trade on, create a checklist which helps you determine what type of market you re looking to trade in. Do not try and ‘force’ trades. This will also help with filtering trades and cashing in on good opportunities.
Forex vs Binary Options
Binary Option’s main advantage over Trading Forex is the defined and limited loss that you can incur on any trade. When you buy a Binary Option you know at the start, what your maximum loss will be.
It is defined by the cost of the option itself. You may also define your loss trading Forex by adding a Stop Loss order to your position, but two things can then come into play;
- A volatile break in price against you where you were planning to stop your losses after, for example, 30 pips, but you end up being stopped after more than 30, due to market volatility.
- The temptation to move your Stop Loss as the market gets close because you feel the momentum is not going to last. In the end this could cause you to lose much more than you had initially thought of risking in the trade.
In other words it can take away the need for disciplined risk management. Often traders end up trading emotionally which can eventually be disastrous. With Binary Options your maximum loss is always fixed and there are no risks of losing more.
This is also connected to the concept of volatility, with a Binary Option it doesn’t really matter how the market moves as long as it ends up in the money at expiry, whereas having a Forex position can often see you take a loss due to the high volatility of the market – to then see the price move back in your favour.
While both trading methods share many common features, there are additional elements that set each apart:
- Leverage. Binary options are generally offered without leverage. Traditional Forex often provides large amounts of ‘gearing’. Leverage is a double edged sword. Some traders will demand the extra profit potential it gives, others will be concerned about the losses that could result in leveraged trades.
- Risk. Risk and reward is clear out the outset with binary options. The best and worst case scenarios are both known. In more traditional forex, the profit or loss may not be clear until the trade is closed. Leverage magnifies this issue.
- Capital requirements. Traditional forex will require more cash on account than binary options.
- Flexibility. Binary options can provide Touch and Range options in a simple way. The same trade profile can be achieved with conventional forex trades, but it needs more thought on behalf of the trader.
- Fixed Expiry. Forex traders can move in and out of trades without a definitive end point on any of them. Binaries require a specific expiry to be set at the start of the option.
- Monitoring. A binary option can be left to mature at expiry, with no additional risk. A forex trade needs to be monitored incase there are sharp price movements that might trigger stop losses or similar. Binaries can of course, be traded throughout as well, so some traders may prefer to monitor binary positions also.
Speed of Trading
Binary Options allow for very short expiry times. Expiries of just a few minutes are available, in fact even as little as a sixty second expiry. In forex it is very rare that the market will move enough for you to close your position in a few minutes let alone in just sixty seconds.
Given that payouts for Binary Options range from 75% to 90% you can buy an option for let’s say, £200 and receive a gain of between £150 and £180 after only a few minutes.
Distance to Target
With Forex trading you enter a position with the aim of the price level reaching a certain target which will inevitably be far away from the current price. Binary Options allow for the target price, the strike, to be at the money, creating higher chances of the Option being in the money at expiry.
With the forex target price potentially far away from the current market price, a larger price move is required in order to profit to the same degree.
In Forex if the current market price for EUR/USD is 1.1200 you enter the trade with the idea of the market going up or down, let’s say 20 pips, whereas in Binary Options the strike price will be the current market price 1.1200 and your option has to be above or below that price even by only 1 pip for you to cash in.
The Advantages of Forex
 The biggest drawback when trading Binary Options is your required win rate. In Forex trading if you are applying risk/reward ratios correctly then your individual profits should usually be higher than your losses.
The biggest drawback when trading Binary Options is your required win rate. In Forex trading if you are applying risk/reward ratios correctly then your individual profits should usually be higher than your losses.
This is because you should be entering each trade with a Target profit that is higher than the Stop Loss, for example 35 pips against 25.
This means that even if you are right only 50% of the time you should be making some money, as your winning trades will earn more than your losing trades.
This concept doesn’t work for Binary options and it’s easy to see why. With payouts of around 75-90%, traders must win more than 50% of their trades in order to be profitable. With each individual trade, more funds are being risked, than will be won in the event of the option finishing in the money. In this scenario you have to be getting it right more than 50% of the time to return a profit overall.
Also, with binary trading there is no real secondary market. Once you have bought an option, you may want to exit that position before the expiry – you may be trying to minimise your loss or maximise your profit if you think the market is changing.
Therefore you may find yourself looking to sell the option you bought. To do that you only have the choice of selling it at the price the broker, where you bought the option, displays to you.
While you could have various accounts with different Binary Option brokers and compare the prices of the option you want to buy before actually buying it, once you are in the trade, if you want to unwind it, that is close the trade before its actual expiry, you have no choice but to do so at the price the broker displays. In Forex of course the market is priced freely at any given moment and you know you will get the fair market price to exit your trade and not the broker’s price.
To sum up the binary options vs Forex debate
Which trading choice is the best i.e. most profitable market to trade in? Binary options or Forex? This depends greatly on your own level of commitment in terms of hours a day in front of a screen and discipline in risk management.
With Binary Options you may not need to be in front of a screen for many hours a day to follow the markets on a constant basis as may be necessary when trading Forex.
You can take your position and wait for the outcome resting assured that your maximum liability is the cost of the option. You won’t have to worry about maintaining your stop loss, it’s fixed at the price you paid for the option and can’t be changed.
One thing that is common to both markets is the analysis needed to make a trading decision. Whichever market you are going to trade in you will always be looking at Fundamentals and/or Technical Analysis. For both markets you will need to hone your analysis skills and create a profitable trading plan or strategy.
Fundamentals of Trading Forex Binary Options
Here, a professional trader, and founder of a money management and trade advisory firm, shares his thoughts on the fundamentals of trading forex binary options and the system he personally uses.
The strategy below is not a secret but it is not well known either. It’s simplicity is the reason for its success.
EUR/USD
The currency pair I generally trade is the EUR/USD pair. This is because it is the most volatile – but also predictable – forex pair. It remains the most traded pair since the opening of the Forex markets to retail investors. Daily volume has increased hugely since those early days. EUR/USD is also pair used by financial firms to hedge revenues against market swings.
One issue the regularly crops up on binary options forums, is the volume of different strategies discussed or offered. The majority of traders think that the more complex the system, the more profitable it will be.
When these forex strategies fail, the system is blamed. The real issue however, is behind the screen. No strategy will adapt itself to evolving market conditions; the trader must adapt.
Many would argue that this strategy will not work in specific market conditions. The point though, is that markets are binary; the price will only go up or down. Ranging markets do not actually exist. Any system has the same ultimate goal – to detect the best entries and exit points for any given trade.
For example: An experienced trader will detect support and resistance levels easily. A beginner may not. The same novice investor might use a strategy using:
- Stochastic,
- MACD
- RSI…
…but what they fail to see, is that these indicators give him the same entry points the seasoned trader uses.
When trading forex binary options, spotting the best entry point and knowing the next price move is key.
Note: The below are personal opinions and a strategy I personally use. Everything should be read carefully. Do not jump to using the high-risk methods without understanding fully how the strategy works.
Consider trading with a demo account before going risking real money. Be prepared to pass up trades if something puts you off. Do not force trades where there are none, opportunities will arrive.
Forex Fundamentals
The first point is to offer an explanation of forex markets in general: Exchange of currencies is ruled by the laws of supply and demand.
Here is hypothetical example: Apple (A US based corporation) sells 1 million handsets across Europe, raking in 500 euros per product. EUR (€) is the base currency. They use HSBC for clearing, so these funds are received there. However – Apple reports in dollars, and their governing account is with BOA.
So Apple made €500m which sits in the HSBC account in Luxembourg. Those funds now need to flow to their BOA account and changed to USD.
They now need to exchange currencies. The transfer order comes in on Tuesday at 4 pm UK time. It will not be transferred immediately. Banks will accumulate all their USD orders during the night. These may have arrived up to a month ago.
The UER/USD pair is trading on Wednesday morning at 6 GMT at 1.27000. So Apple’s account with BOA will receive 635 million USD at 8 am EST. The order is fixed at 1.27000. How can banks – or retails investors – make money from this transaction?
How Do Investors Profit?
BOA will obviously get a commission from Apple, but what of HSBC?
At 8 am GMT – the opening of the London Markets, the liquidity is 380 million euros. The price is 1.27010. So 500 million euros is equivalent of 635 050 000 USD. At present, the markets cannot handle this trade.
Extending the hypothetical example, here is how the markets look. Euro outlook is bullish. Asian markets rose during the night. The US fiscal cliff is getting resolved. Millions of retail investors and outlets take BUY orders and place their stops 10 pips under the current price. There is now pending liquidity of 300 million euros plus current liquidity of 380 million euros. Total liquidity then, in USD on the market at the moment is (1.27010) 482 638 000 USD and 381 030 000 USD pending (equivalent of stops).
Currencies Exchanged
Market data shows that the stops are at 1.26910. So at 8.15 am GMT, the order comes to SELL the available liquidity (840 Million Euro sell order). The effect of this is to push the price to 1.26905. Now, the bank’s BUY orders are triggered. Other retail investors now make new buy orders to cover their losses.
The price flies to 1.27099. Here, we might exit our BUY positions gradually (assuming we followed the bank trades). As the trend still seems strong, people buy our orders. On a chart this might be shown by green candles getting smaller in size after upwards trend.
Trade Outcome
So market liquidity rose to 380 + 300 = 680 million euros. We exited at 1.27099 for a profit of 9.9 pips (from 1.27000). Once leverage is considered – and the sheer scale of these trades – huge sums of money have just changed hands. Banks (and retail investors) both utilise leverage to make big gains from such moves.
This was all purely an example. The truth is that the volumes are huge (4 trillion USD daily). There are a lot of traders, market makers and stakeholders in these markets, but that example is to show you how FX works, and this is fundamental when analysing support and resistance (SR) levels and trends.
These levels are defined by the larger players. They also hold really well because retail investors spot them and use too. The smart money cycle happens in 3 price cycles. We then see a short-term channel where the price is stuck for a bit accumulating strength.
A Forex System – Fibonacci
These price cycles are not random. They follow a sequence. This sequence is defined by a set of numbers called Fibonacci numbers.
Fibonacci numbers were not developed for trading. They occur throughout the natural world, where many biological systems can be described in terms of Fibonacci-like sequences.
Major forex traders (including banks) don’t use indicators like RSI, CCI or MACD. They use systems based on the Fibonacci numbers.
Combining Fibonacci with precise price channel calculations and information on how others trade, you have a profitable trading strategy for forex.
Forex Using Binaries?
Why would you consider all this when trading binary options? Well unlike with spot foreign exchange, you need to be right more often. You need to identify the direction, not the size of the move.
During day trading this will not involve big trades shown above. I want to bag price movements (and pips), so I need to use something that finds these price cycle moves and reversals. For binary forex (and spot fx day trading) I use 3 indicators with very precise functions.
Forex Correlations
Forex correlations are a key tool. If you have not learnt what they are – It could already be harming your trades. Correlations show which pairs move together. Also, it pinpoints those that move in opposite directions. No less importantly, it will show which pairs are unrelated.
This all helps to judge which trades we should take. It can mitigate risk, and also provide additional trading opportunities not obvious on the price chart.
How To Read Exchange Correlations
Correlations are normally displayed with values ranging from -100 to 100. A value of -100 (inverse correlations) show two forex pairs that move exactly opposite each other. If one rises, the other falls and vice versa.
A figure of 100 means two forex pairs move together. If one rises, the other also rises. Likewise, if one falls the other will also. Figures at the extremes of the spectrum are rare – but the closer the number to -100 or 100, the stronger the correlation.
So figures over -/+ 70 are a noteworthy correlation. Anything over -/+80 is a strong correlation. Consider the GBP/USD and EUR/USD crossover above. It gives a figure between the GBP/USD and EUR/USD of 89.6. This shows a strong correlation.
Next, judge USD/CHF with EUR/USD. It shows that the correlation between these two pairs is -95.4. This highlights a very strong inverse correlation. When the EUR/USD goes up, the USD/CHF goes down, and vice versa.
With plenty of pairs, there is no relevant correlation. Where a value (positive or negative) is less than 60 the correlation is not very strong. Anything around 0 shows there is no correlation between the pairs at all. As an example the NZD/USD and the EUR/USD pairs.
The correlation here is -1.7. This means there is no discernible correlation, on a daily basis, between these pairs. In other words, the NZD/USD rising or falling tells us absolutely nothing about what the EUR/USD might do.
Correlation Ranges
Correlations tables are created and updated based on hourly, daily and weekly timeframes. All these timeframes provide valuable information depending on what timeframe you trade on. For short-term trading, the hourly and daily correlations will be the most important important. Figures change, so do not take the above as gospel.
Why Forex Correlations Matter?
There are a range of reasons to care about forex correlations. The biggest reason I monitor them is to control risk. For example, a trader might assume trading multiple pairs has offered them diversification. Only by knowing pair correlations, can this be assured.
If you go long (buy calls) in the EUR/USD, GBP/USD and sell (buy puts) the USD/CHF you have essentially taken 3 very similar positions. If one moves against you, they are likely to all go against you. Risk has effectively been tripled. If leverage has also been used, the risk is large.
Another reason why forex correlations matter, is that they can provide you with trades you may not have seen. For instance, you believe the EUR will appreciate against the USD (ie. the EUR/USD will go up). You look at the chart and don’t see a great trade set-up. Since you know that the GBP/USD typically moves with the EUR/USD (based on the current correlation), you can also check out the GBP/USD to see if there is a better trade set-up.
You may also want to see if there is a trade set-up to go short (buy puts) in the USD/CHF since it typically moves in the opposite direction of the EUR/USD. High correlations (positive to negative) provide you with alternative trades; choose the one with the best trade set-up.
Confirm trades
I also like to use forex correlations to confirm trades. Upon finding forex pairs with high correlations, I will use one pair to confirm trades in the other. For example, if the EUR/USD is rising, and I want to go long (buy calls), I also want to see the GBP/USD rising. As these pairs are highly correlated they should be moving together. When they do not, it warns me that maybe I should look more closely at my trade. It doesn’t mean I won’t take the trade. These correlations do change and two pairs never move perfectly in harmony. It does mean I better have very good reasons for taking the trade (as you always should anyway).
Correlations can be a complex statistical topic. Hopefully this introduction has given you enough of the concepts to do a bit of homework on your own. Check correlations frequently to be aware of relationships between forex pairs which may be affecting your trading.
Use the correlation data to control risk, find opportunities and filter trades. If you are having trouble seeing how correlations work, try looking at the figures in the correlation tables and then pulling up price charts of the two forex pairs in question. Notice how the pairs move relative to one another; doing this will help create a general understanding of correlations.
Swing Trading – Definition and Examples

A “swing” trade is generally a trade that is open for between one and five days. A trader is attempting to follow the momentum of an asset price, usually within an established trend channel.
The idea of “swing trading” comes from the stock market and is a type of trading strategy followed mostly by retail traders. The reason being that it is difficult for institutional traders to put on positions of the sort of size they need without moving the market.
This may not necessarily be true for the Forex market as the Major pairs are all very liquid, and there is a vast interbank market. Traditionally swing trading positions itself in terms of time horizon between that of day traders and medium term investors or traders. A day trader will hold a position for a few seconds or hours at the most while a medium term investor may hold a position for several weeks.
Forex is Different
However, the forex market is a very different type of ball game. Even in the most raging bull trend or most savage bear trend you may still find the day’s price action has gone through a couple of highs and lows, instead of heading in one direction for the whole day.
Swing traders in Forex markets may also well be day traders, trying to take advantage of price momentum to the down and upside. Their mission is to get into the market long as momentum rises to the upside but go short as soon as the market swings round again to the downside.
What is the analysis behind the Swing strategy?
Swing traders, due also to their short holding period, are not so interested in fundamentals and are primarily focused on technical analysis. It may be something as simple as a 3 day moving average crossover strategy, tweaked to get in and out of positions early. Or a more elaborate mixture of various technical indicators superimposed upon each other.
In any case, the intention is the same, to get in early when the momentum changes and to turn the position around when the market retraces. This strategy, therefore, works particularly well when the market is trending sideways rather than up or down.
Forex markets do have many swings even when the market has a clear trend, but attempting to sell in a strong bull market early enough to catch the swing may prove painful.
Defining the right market
Defining whether the market is currently suitable, over a given time frame is crucial to the successful outcome of this strategy. You have to consider the time horizon you are trading over, in Forex markets swings happen in comparatively shorter time intervals. It is, therefore, necessary to stick to the time horizon you are trading in to determine if the market is trading sideways. A sideways market is defined when highs and lows do not go past previous highs and lows, giving rise to so-called channels as well as other chart patterns.
The shorter the time frame the smaller the difference between high and low, or the shorter the channel of price action. For day charts, you can expect most majors that are drifting rather than trending to have between 2% and 6% wide channels. In comparison, if you are looking at an hour chart the channel might be more like 0.5% to 1.5%. Often sideways markets in time periods that are less than one day can move in very tight ranges as the market consolidates its new level.
Let’s look at a couple of examples
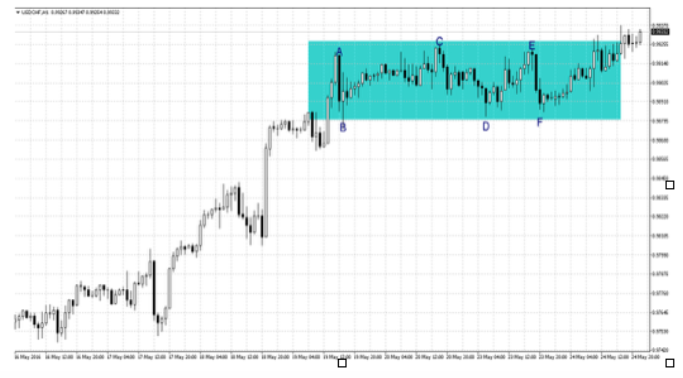
The hourly candle chart in the first image is for the USDCHF. As we can see, the pair goes through a relatively tight price range of around 45 pips, between 0.98800 and 0.9925. The blue rectangle that goes from May 19 06:00 am GMT to May 24 03:00 pm GMT, highlights how channeled price action remained throughout that period. The swing trader’s job then is to attempt to go short or sell at points A, C, and E and go long or buy at points B, D, and F.
In swing trading, there are no downtime periods; the strategy consists in being long or short continuously. So there are no close and wait periods, which can be useful when the market is retracing allowing you to get back in the market at a better price than the one you exited at.
However, it can be excruciating if the trend is sharp and continued.
It is, therefore, necessary to identify a break of the sideways price movement, and the development of increased momentum in one direction. From the chart above it looks like there has in fact been a break-out of the channel pattern.
Three of the last four bars have closed above the blue rectangle which should raise red flags to a swing trader. The sideways action may not have evolved into a new uptrend. However, the fact the price has moved above its channel should create caution.
It would be necessary to wait and see if the market has now found new momentum or simply a higher top side to the channel.
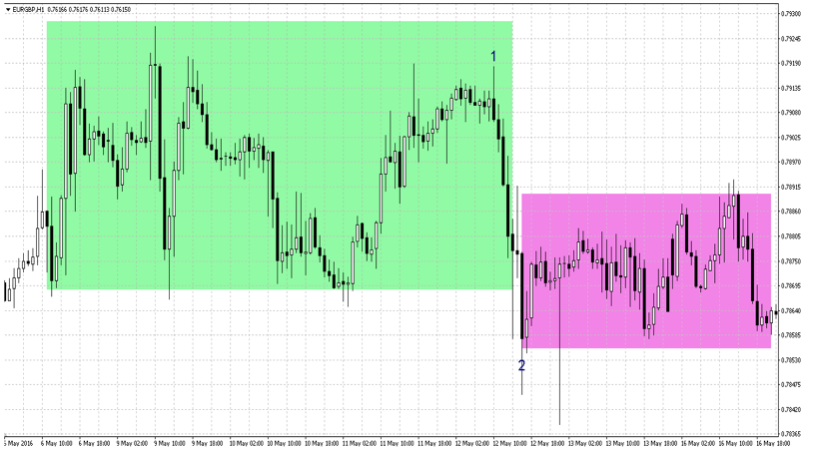
The hour chart in the second image, for EURGBP, shows how price action moves from one sideways channel in the green rectangle to another sideways channel at a lower level in the pink rectangle.
As price moves from point 1 to point 2, it may be tempting to open a short position at point 2 with the view that a new bear trend is underway. Only to find that price is now heading back higher again and trading within a range.
Ultimately caution has to be used as always, but even if you’re not a swing trader identifying a sideways market will help not getting caught out on swings. Correct identification of market regime will allow you to avoid buying when the market is about to turn down, or selling when the market is about to retrace back up.